Can you build an extended, interactive lesson in Moodle?
Yes!
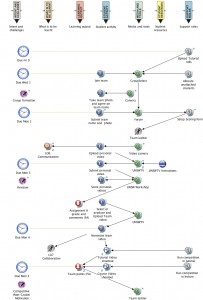
I’ve seen (and set up) some quite complex sequences. The activity mapped out here engaged students over several weeks; several meetings of teams, individual, small group, large group and plenary work; and was highly active and personalised.
After a team selection and formation activity, individual students submit a short video (explaining a revision topic) for peer assessment, and review several others for correctness and effective communication (inter alia). Each team chooses and submits their best video to a shoot-out in a tutorial for team points; and the best of each tutorial goes into a shoot out in a lecture for team points. The video collection provides revision resources for the next cohort.
However…
Complex, extended learning designs are hard to maintain, and hard to migrate to a different platform in the future. How portable is the learning design (to the next version of device, browser, or LMS)? How soon will it appear maladapted to incoming learners? How many people are competent to revise it? How costly is it to modify and test as the curriculum or content changes?
And perhaps more importantly, can it flex for students with unique needs or circumstances?
Acknowledgements
The course design illustrated was originally developed and piloted by Waldron, Kinkaid and Whitty for UNSW Australia.
Illustration prepared with CompendiumLD, Open Learning UK’s special purpose adaptation of the open-source software Compendium, available from http://compendiumld.open.ac.uk/